It starts with an idea
If the Manufacturer has an idea for a new device or machine, it will most likely have an enclosure or cover. It used to be that most enclosures were made of sheet metal. Nowadays, an increasingly common material is plastic (aka plastic). Why? Because plastic is lighter than sheet metal so even large covers and enclosures help reduce the weight of the entire device.
The plastic additionally has specialized technical parameters that allow it to be used in the medical, electronic, automotive or even agricultural machinery industries. UV resistance, weather resistance, high impact resistance, electrostaticity or a specific degree of non-flammability are just some of the current requirements for plastics. It also allows a wide choice of colors and surface textures, and the fact that it is tinted in the mass means that even mechanical damage is not as visible as on painted sheet metal.
Good design is key
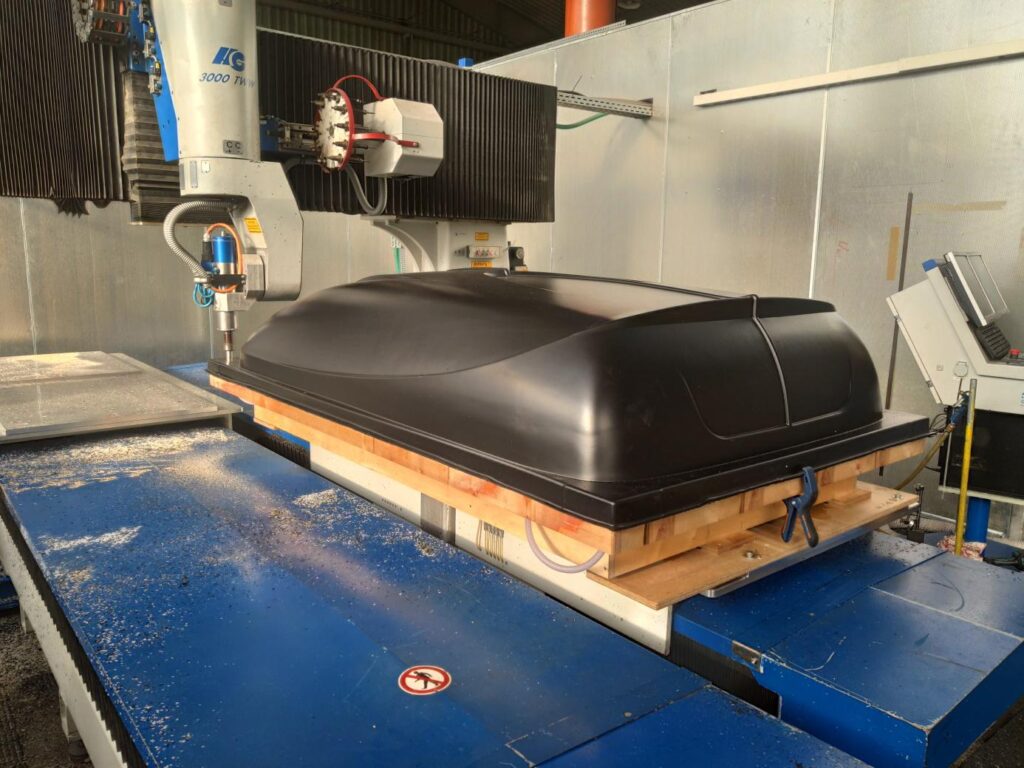
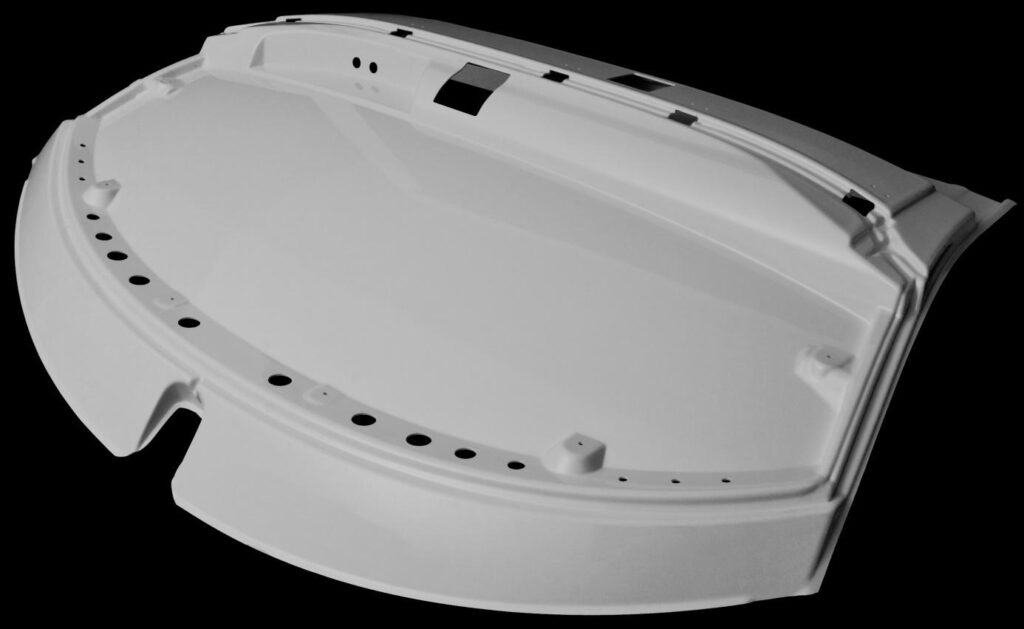
In order to make a detail, we must have a 3D technical drawing, which will contain all the information, dimensions and details. If there is no design then we will be happy to make it by adapting it to the thermoforming technology. Vacuum thermoforming involves heating the plate to the right temperature so that it becomes plastic, and then using a mold to give it the right shape.
The most important consideration when designing for this technology is the mandatory slope of the walls so that the detail can be removed from the mold and the starting thickness of the plate. Thickness is important because when shaping by thermoforming, the material is stretched, and thus the walls are thinner. That’s why it’s so important to properly match the thickness of the board to the expected thickness of the workpiece.
Prototype
The idea of a prototype is to refine the ordered component in such a way that changes and possible corrections can still be made before the start of mass production. Prototypes are shaped on molds made of MDF, as they allow changes to be applied. After 1 piece of prototype is made, it is sent to the customer for approval.
The automotive industry also often uses the so-called “automotive”. preseries, or a certain number of items that are subjected to transportation tests. Only after the preseries have been approved and all performance characteristics have been verified is final approval given. Once the prototype is officially approved, you can proceed to the most important stage: making the aluminum mold.
The most important thing is the form
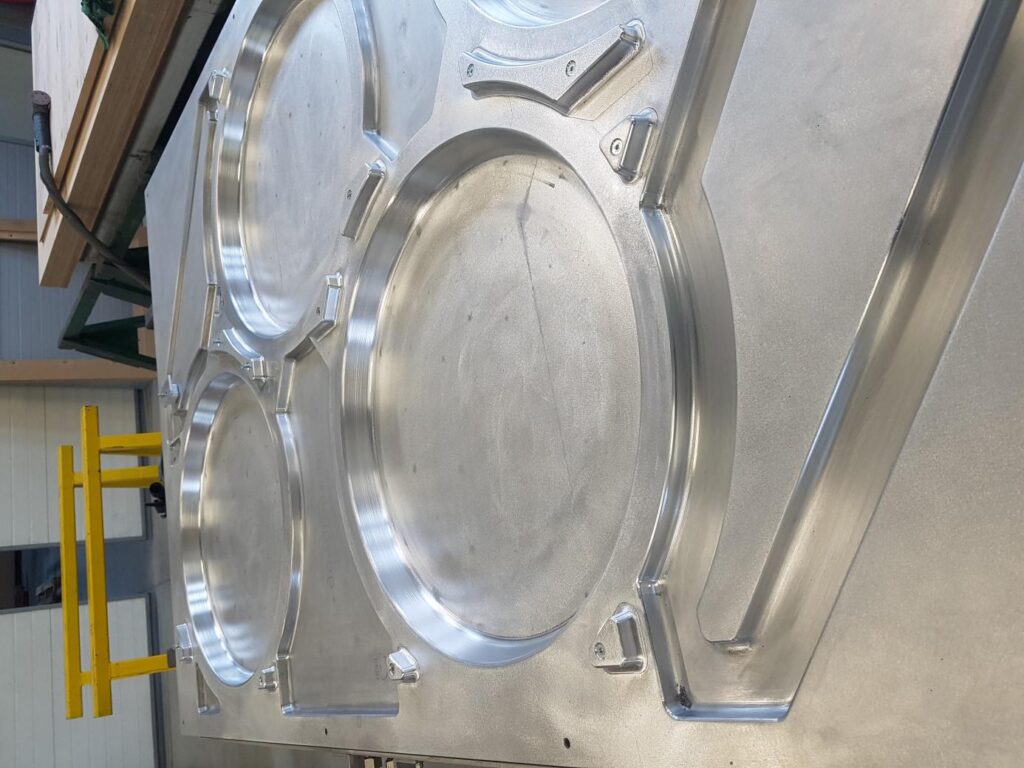

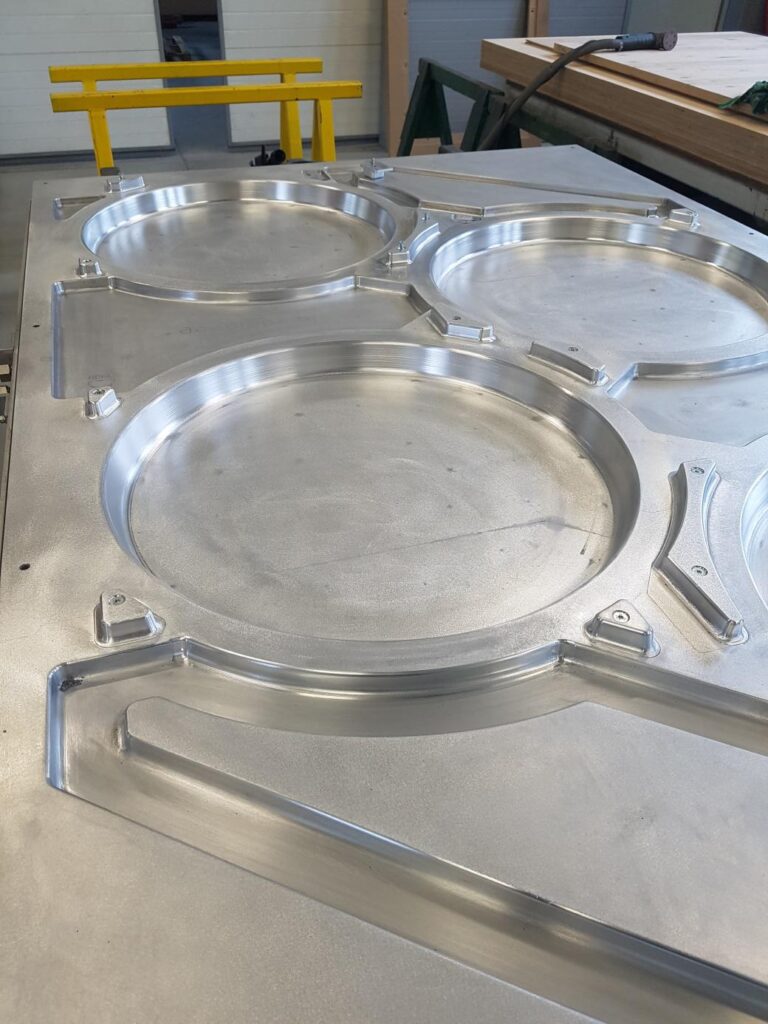
Yes, the mold for mass production is most important. It is she who guarantees the repeatability of mass production and the shape according to the design. The most difficult thing is to control the behavior of the heated plate during the time when it is plastic. Maintaining the right, constant, controlled temperature during shaping allows the part to be made in the same shape from the first plate as from the last. Temperature control is done with a system of water tubes mounted under the mold.
It is the high serial repeatability that makes the best type of thermostated mold an aluminum mold. Temperature control is done with a system of water tubes mounted under the mold. The molds can also be made of other materials. However, they have a certain number of limitations whether in terms of quality or cost, which make production at the aluminum mold the most optimal in terms of price.
Vacuum thermoforming of plastics is gaining popularity. The high repeatability also makes it possible to reduce the price of the part due to low scarcity during production.
Series production
The start of mass production is the most important stage for both the Employer and the Contractor. That’s when the moment everyone is really waiting for arrives. It is then that the purchaser can proceed to install the covers on his device, and the Contractor has the satisfaction of having contributed in some way to the creation of a new product.